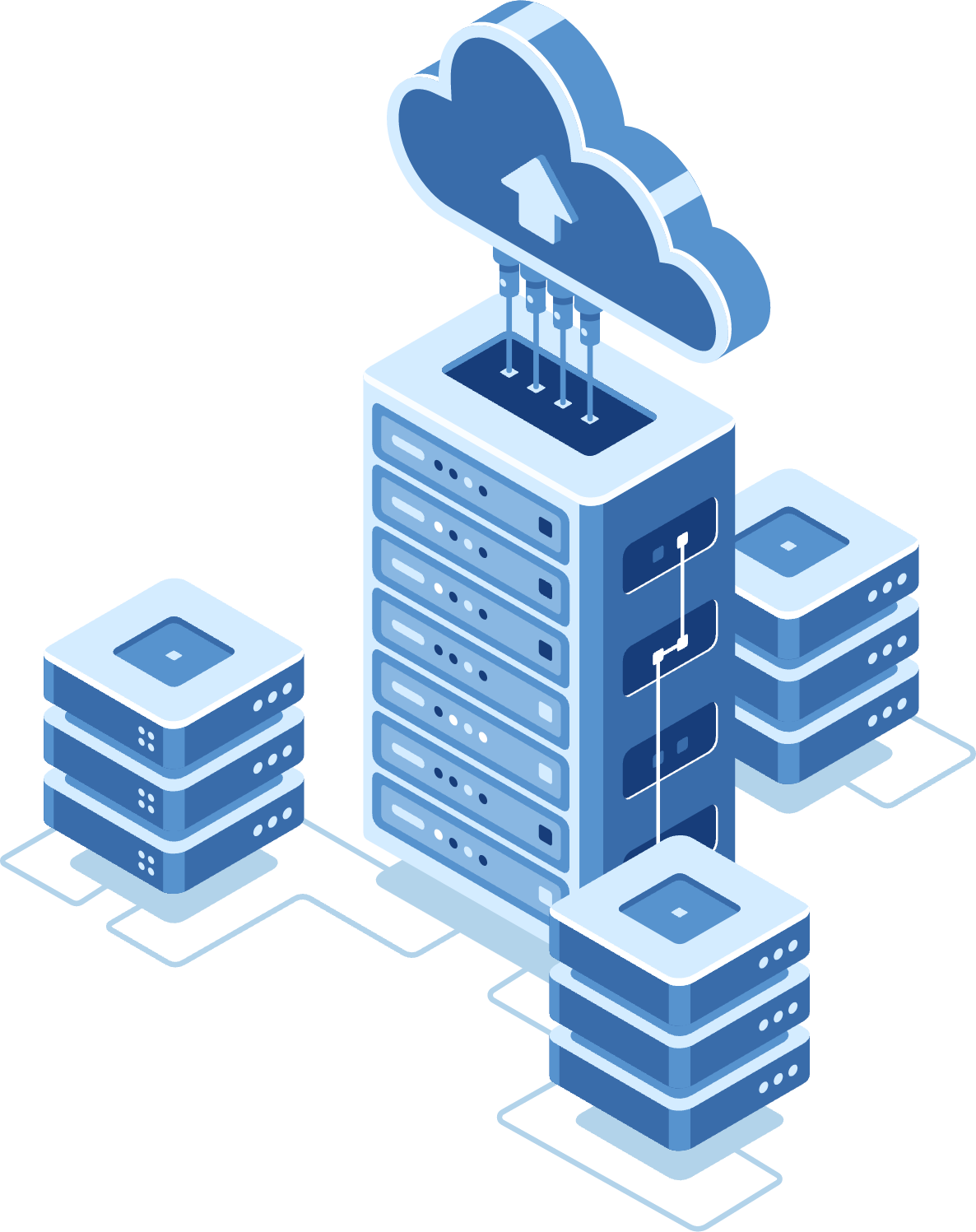
Elevate Business with Premium Cloud Server Solutions!
Our scalable services grow with your business, ensuring seamless support, robust security, and reliable backups. Discover our Cloud Server Solutions today!
Custom Solutions
With Advika Cloud Simplify, Streamline, and Accelerate Your Business
Get Quick
24x7 dedicated network operation center to resolve all your queries or issues
Futuristic Approach
Prioritizing digital transformation and technological advancement
Advika's Technological Superiority
We are the pioneers in Cloud Server and Dedicated Server services in India, offering highly affordable and reliable server solutions to our customers. Here are some key highlights of our presence and achievements.
- Fastest-growing server provider with over 5,000 trusted and satisfied subscribers
- Strong presence across 50 cities nationally and 12 international cities

12+
Cities globally
50+
Cities Nationally
24+
Years of Excellence
Our 4'S Philosophy
Availability
of the networks.
Adaptability
to meet customers demands.
Acceptability
to preferred uptime.
Affordability
for customers.
Why AdvikaExplore Our Impressive Stats!
3500+
Trusted EB Customers
1000+
Global reach
24x7
Customer Support
4.7
Ratings at Google
99.9%
Uptime & Availablity
30+
Awards & Recognitions
Our Achievements
Our Data Center Certificates
Awards



We Partner with the best
Technology Partners
Internet Partners
Hardware Partners
Do you have a query?Book a Call

For further queries
Please get in touch with your dedicated account manager or reach out to us on